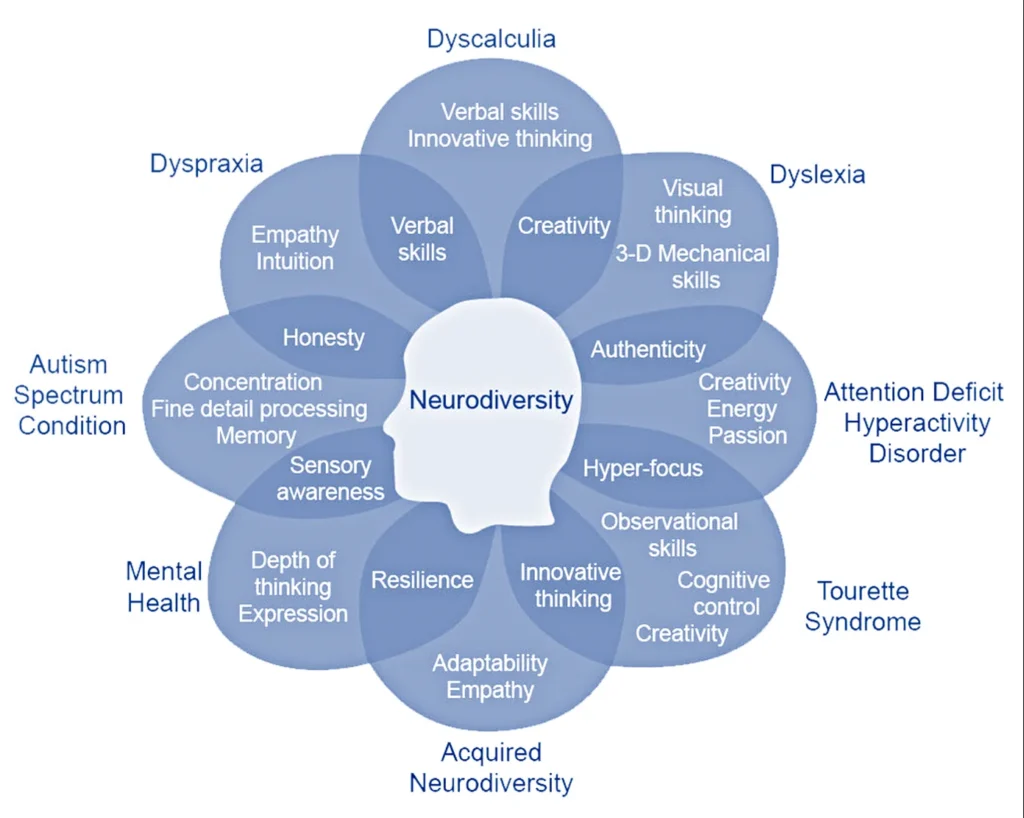
Neurodivergence is a multifaceted concept that goes beyond the commonly recognized conditions of ADHD and autism. While these are certainly significant aspects of neurodiversity, the spectrum encompasses a variety of brain differences that many individuals experience without fitting neatly into specific diagnostic categories. If you’ve ever sensed that your cognitive processes diverge from the typical, you may find resonance in the nuanced signs of neurodivergence. From unique sensory sensitivities to distinct emotional processing, understanding the breadth of neurodivergence can illuminate the diverse ways our brains operate, encouraging a deeper appreciation of individual differences.
| Signs of Neurodivergence | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Sensory Sensitivities | Experiencing overwhelming reactions to sensory inputs like bright lights, loud noises, or certain textures. |
| 2. Internal Dialogue | Having a constantly active internal monologue that can be exhausting or distracting. |
| 3. Executive Function Challenges | Struggling with planning, organizing, and completing tasks, which can occur without ADHD. |
| 4. Intense Emotions | Feeling emotions deeply, which can lead to both empathy and emotional exhaustion. |
| 5. Communication Differences | Having difficulty with spoken communication but excelling in written or non-verbal forms. |
| 6. Unique Perception of Time | Struggling to estimate time or feeling disconnected from schedules and deadlines. |
| 7. Face Recognition Issues | Difficulty recognizing faces (prosopagnosia), relying on other cues for identification. |
| 8. Learning Differences | Having unique ways of processing numbers or reading, like dyslexia or dyscalculia. |
| 9. Hyperfocus | Becoming deeply absorbed in specific topics or activities, sometimes losing track of time. |
| 10. Alternative Learning Preferences | Preferring hands-on experiences or visual aids over traditional learning methods. |
| 11. Disconnection from Social Norms | Feeling confused by social rules and drained by social interactions. |
Understanding Neurodivergence
Neurodivergence refers to the various ways our brains can differ from what is considered typical or ‘neurotypical’. When people hear this term, they often think of ADHD and autism, but the truth is that neurodivergence includes a wide range of conditions and experiences. These differences can affect how someone thinks, feels, or interacts with the world around them. It’s important to recognize that everyone is unique, and our brains can work in many fascinating ways.
Some individuals may not have a formal diagnosis but still experience neurodivergent traits. For instance, you might feel overwhelmed by loud noises, have trouble focusing, or find it hard to understand social cues. These experiences are valid and highlight the diversity of the human brain. By understanding neurodivergence, we can foster a more inclusive environment that celebrates all types of thinking and learning.
Sensory Sensitivities: More Than Just Autism
Many people think that sensory sensitivities are only associated with autism, but that’s not true. Sensory processing issues can occur in various conditions, including anxiety or OCD. For example, some individuals might feel irritated by certain textures like scratchy clothing or feel overwhelmed in bright lights. These experiences can make everyday life challenging when sensory input feels too intense.
Recognizing sensory sensitivities is crucial because it helps us understand how different people interact with their environment. If you often feel stressed in loud places or need a quiet space to think, you might be experiencing sensory processing differences. Being aware of these sensitivities can lead to better support and accommodations, allowing everyone to feel more comfortable and focused.
The Challenge of Executive Functioning
Executive functioning is a term that describes how we plan, organize, and complete tasks. While many associate difficulties with executive function primarily with ADHD, other conditions can also affect this ability. For instance, anxiety or depression can make it hard to start projects or manage time effectively. If you find yourself forgetting important deadlines or struggling with organization, you might be experiencing these challenges.
Understanding executive dysfunction helps us realize that it’s not just about being disorganized; it’s about the brain’s ability to manage tasks. Many neurodivergent individuals can excel in certain areas while struggling in others. By acknowledging these differences, we can create supportive environments that help everyone succeed, regardless of their executive functioning abilities.
Intense Emotions and Neurodivergence
Emotions can feel more intense for some individuals, especially those who are neurodivergent. While everyone experiences feelings, some people might feel joy, sadness, or anger much more deeply. This heightened emotional sensitivity can be a double-edged sword, allowing for great empathy and creativity but also leading to emotional exhaustion. If you find that your emotions often overwhelm you, it might be a sign of neurodivergence.
Understanding this aspect of neurodivergence can help in managing emotions better. Recognizing that intense feelings are a valid experience can encourage individuals to express themselves creatively or seek support. It is essential to create spaces where people can share their emotional experiences without judgment, fostering a supportive community.
Communication Styles: More Than Words
Communication can take many forms, and not everyone finds it easy to express themselves verbally. Some neurodivergent individuals may struggle with speaking but excel in written communication or art. This can be particularly true for conditions like dyspraxia or social anxiety, where verbal expression feels challenging. If you prefer writing over talking or often feel misunderstood in conversations, you might have a unique communication style.
Recognizing different communication styles is vital for creating an inclusive environment. It allows everyone to express themselves in ways that feel comfortable for them. Encouraging alternative forms of communication, such as writing or visual aids, can help bridge gaps and foster understanding among people with various neurodivergent traits.
Unique Relationships with Time
Time can be tricky for some people, especially those who are neurodivergent. While many people follow a schedule easily, others might find it hard to estimate how long tasks will take or struggle with being punctual. This can happen for individuals with dyslexia, dyspraxia, or even anxiety. If you frequently lose track of time or feel overwhelmed by deadlines, you might be experiencing a different relationship with time.
Understanding how neurodivergent individuals perceive time can lead to better strategies for managing tasks. Using tools like timers or reminders can help make time management easier. By acknowledging these differences, we can support each other better, ensuring that everyone can navigate their day-to-day tasks more effectively.
Learning Preferences That Challenge the Norm
Everyone learns differently, and neurodivergent individuals often have unique learning preferences that don’t fit traditional methods. For example, some might thrive with hands-on experiences or visual aids, while others may need extra time to digest information. If you find that standard classroom settings don’t work for you, it could indicate a different way of learning that aligns with neurodivergence.
Recognizing and embracing diverse learning styles is essential for creating an inclusive educational environment. By allowing students to explore alternative methods, such as project-based learning or interactive activities, educators can support neurodivergent individuals in reaching their full potential. This understanding can lead to more successful learning experiences for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is neurodivergence?
Neurodivergence refers to various brain differences, including ADHD and autism, but also includes conditions like dyslexia and anxiety. It reflects how individuals think and process information uniquely.
Can sensory sensitivities indicate neurodivergence?
Yes! Sensory sensitivities, like being overwhelmed by bright lights or loud noises, can suggest neurodivergence, even if one doesn’t have a formal diagnosis.
How does neurodivergence affect communication?
Neurodivergent individuals may struggle with verbal communication, preferring to express themselves through writing or art. This can be linked to conditions like dyspraxia or social anxiety.
What does executive dysfunction mean?
Executive dysfunction refers to challenges in organizing, planning, or completing tasks. It can occur in various neurodivergent conditions, not just ADHD.
How do emotions relate to neurodivergence?
Some neurodivergent individuals experience emotions more intensely, leading to strong reactions. This can enhance empathy but also make emotional regulation challenging.
What is hyperfocus in neurodivergence?
Hyperfocus is when someone becomes intensely absorbed in a specific topic or activity, often losing track of time. This can be a trait of neurodivergence.
Can learning preferences indicate neurodivergence?
Absolutely! Neurodivergent individuals might learn best through hands-on methods or visual aids, rather than traditional teaching styles, highlighting unique learning preferences.
Summary
Neurodivergence includes various brain differences, not just ADHD and autism. People can be neurodivergent without a formal diagnosis, showing signs like unusual sensory sensitivities, intense emotions, and unique communication styles. They may struggle with executive functions like planning or organizing tasks, process time differently, or have specific learning preferences that don’t fit traditional methods. Additionally, some individuals may face difficulties in recognizing faces or remembering names. Understanding these traits helps in recognizing the diversity of neurodivergent experiences, promoting acceptance and tailored support for all individuals.